Your basket is currently empty!
General information
With which other signals can G.hn be used in parallel on a coaxial cable?
Coaxial cables are characterised by high quality. They enable data transmission in a very wide frequency spectrum. Several signals are transmitted in parallel in different frequency ranges.
G.hn uses the frequency range 2-200MHz for data transmission.
G.hn can therefore be transmitted in parallel to SAT-TV (950-2200MHz) and to DVB-T2 (470-690MHz).
Parallel use with cable TV (DVB-C) in the frequency range 258-862MHz is also possible. In this case, a 258MHz high-pass filter (at the output of the house amplifier) must be used to avoid interference in the cable network. See the separate point below.
Simultaneous use with Cable Internet (DOCSIS) on one cable is not possible because Cable Internet occupies the entire terrestrial frequency range 5-862MHz. For networking with our devices, the Internet reception must be separated from the coax data network. See the separate point below.
How is the connection between the modems made?
In order for the modems on different cable strands to communicate with each other, there must be a connection between the individual cables.
Different options are possible:
- Terrestrial (5-862MHz) coaxial splitters such as Axing BVEx-01P series (1 input and 2-8 outputs).
- Broadband capable SAT multiswitches and splitters (5-2400MHz).
- SAT multi-switches of any type. For optimum use, please see our notes on multi-switches.
- SAT/TERR combiners. These also enable data networking in conjunction with LNBs without multi-switches.
Of course, data connections via feed-through sockets on the same cable harness are also possible.
In my coaxial cabling, the full G.hn bandwidth is not achieved or no connection is made at all.
Our devices operate in accordance with the G.hn Wave2 specification and use the 2-200 MHz frequency range for data transmission. In order for the data connection between devices to be possible, these frequencies must be open and free from other signals. We use very powerful G.hn chipsets: up to approx. 35dB attenuation on the line, the full bandwidth of 1.5Gbit/s is achieved, at 45-50dB – approx. 1Gbit/s, at 75dB – still approx. 100Mbit/s. Please note the following practical tips.
Do you use a coaxial distributor to connect the individual cables?
We recommend distributors with decoupling (attenuation) between the outputs up to max. 20-25dB. E.g. Axing BVE x-01P series for terrestrial applications (5-862MHz).
Do you use a SAT multi-switch?
Follow our tips for the multi-switch.
Are you using an LNB without a multi-switch for SAT reception?
Follow our tips on the LNB.
In any case, please note our tips on antenna sockets.
Where can the recommended coaxial accessories (combiners, high-pass filter) be obtained?
You can obtain this directly from us or from specialist internet retailers.
Use of SAT multi-switches and LNBs
Which SAT multi-switches are suitable for data networking?
Basically, all types of SAT multi-switches (also Unicable) are suitable.
Can a G.hn modem be connected to the terrestrial input of the multiswitch?
This is possible if the terrestrial input is passive (without amplification) or can be switched passively. The input should be open for frequencies 5-862MHz.
An active terrestrial input (with amplification) is unsuitable for connecting a G.hn modem.
For the technical data on the TERR input of your multiswitch, please refer to its data sheet. Example for three multiswitches from Spaun:
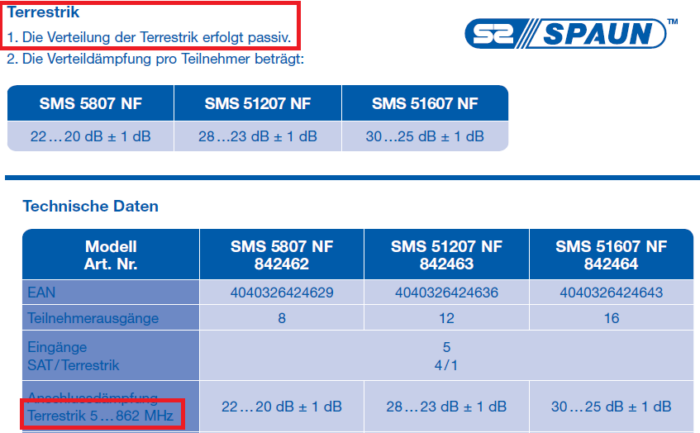
The problem of an active TERR input can be avoided by connecting the modem directly to a free subscriber output. If all outputs are occupied, a SAT/TERR switch can be used, the modem is then connected to the TERR input of the switch:
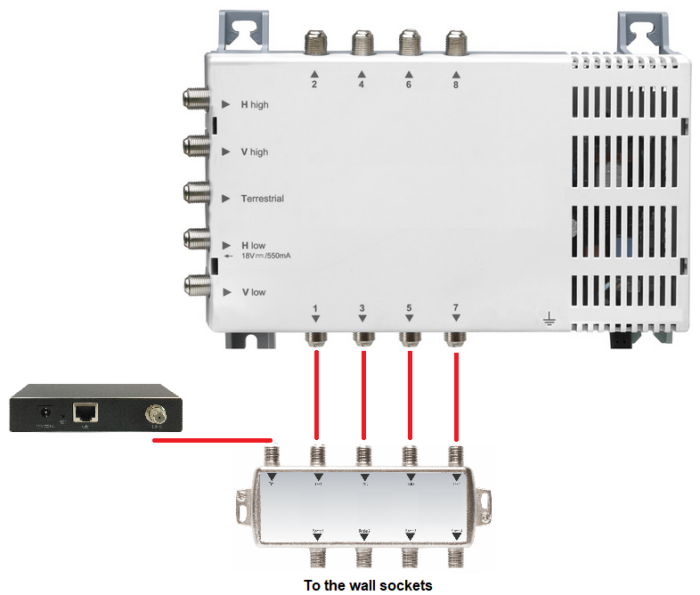
Does the data transmission between the subscriber outputs of the multi-switch work?
Yes, this is always possible and also necessary for home networking, because our InHome modems communicate directly with each other in the network for best possible performance (peer-to-peer).
However, the achievable data bandwidth depends largely on the decoupling (attenuation) between SAT outputs of the multi-switch. This should be taken into account, because for G.hn connections the following applies in general: up to 35dB attenuation the performance remains constant at approx. 1600MBit/s, at 45-50dB approx. 1000MBit/s are available, at 75dB – still approx. 100MBit/s.
There are many different SAT multi-switches on the market. The manufacturers usually state the decoupling specifications in the data sheet. Example for Spaun devices:
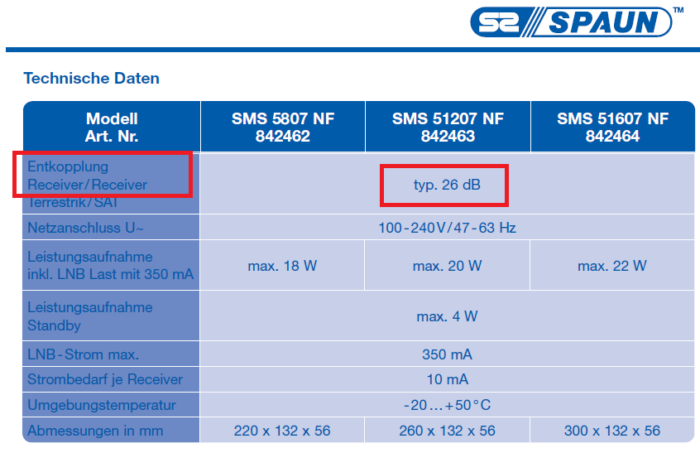
In practice, the following result can be expected:
- With low to medium decoupling (<25-30dB), the modems can reach the maximum bandwidth of approx. 1600 Mbit/s because the total attenuation between the antenna sockets does not exceed 35dB.
- With high decoupling (>30-35dB), the attenuation between the antenna sockets will be more than 35dB, the data bandwidth will therefore be smaller. To increase it, SAT/TERR feed crossovers can be used, these usually have only about 20dB decoupling between the outputs.
The switch is used as follows:
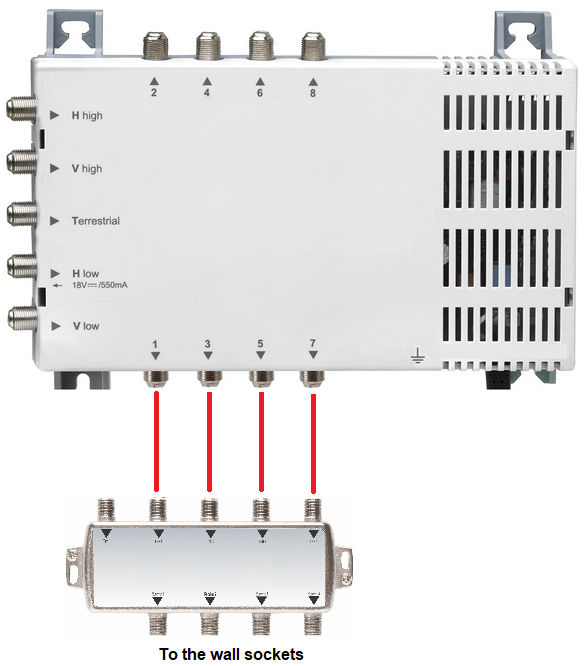
Can via a multi-switchseveral separate data networks be set up (home networking in apartment building)?
Yes, this is possible. In a multi-party house, each party can network the antenna sockets within its own flat via the multi-switch, SAT TV remains intact.
For this, SAT/TERR feed-in crossovers and high-pass filters with DC pass-through must be used. They are used as follows:
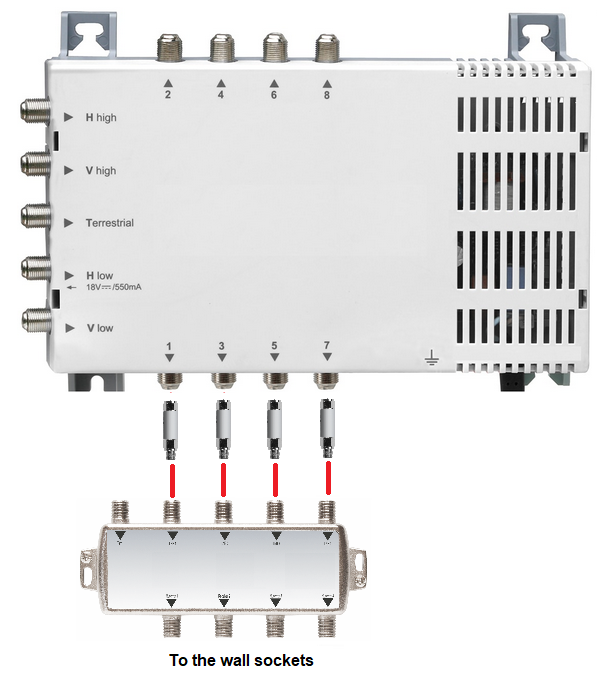
To network more than 4 antenna sockets, several turnouts can be used. They are connected to each other via their TERR inputs.
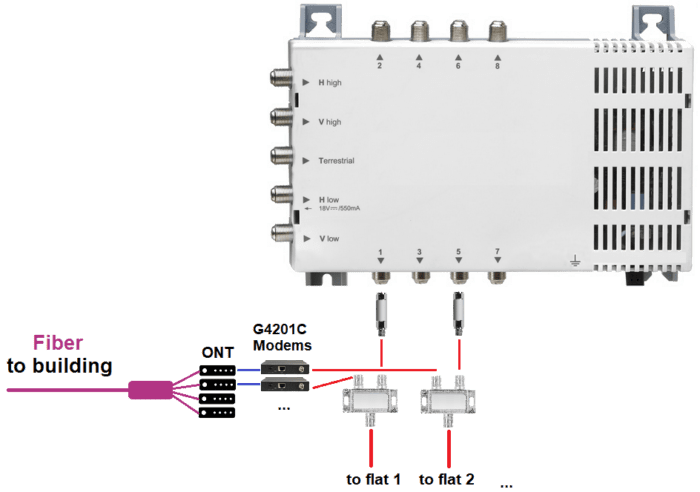
Can via a multi-switchseveral several fiber connections be forwarded (fiber distribution in apartment house)?
Yes, this is possible. In a multi-party house, each party can forward the signal from the ONT to their own apartment and SAT-TV remains intact.
SAT/TERR feeds and high-pass filters with DC pass-through must be used for this. The modem is connected to the TERR input of the feed, the SAT connection to SAT input:
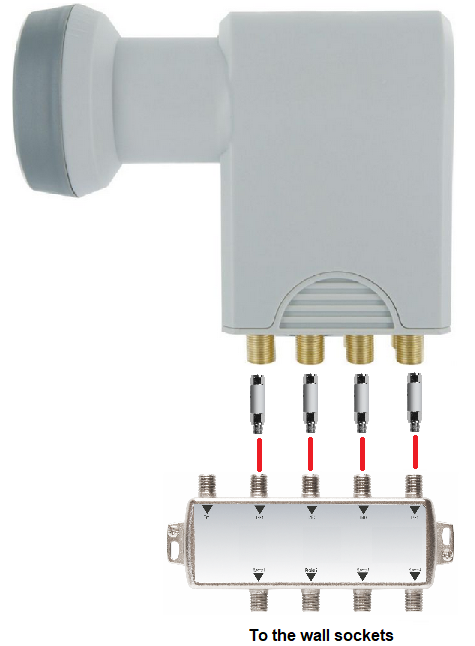
Is data networking with LNBs (Twin, Quad, Octo) possible without a multi-switch?
Yes, this is possible.
In addition, a SAT/TERR combiner is required. The cables from the LNB are routed through the combiner. This creates a fast data connection between all outputs. Several combiners can be connected to each other via their TERR inputs.
High-pass filters with DC pass must be fitted to the SAT inputs of the combiner to avoid interference between the LNB and G.hn.
Use of antenna sockets
Can the modem be connected directly to the coaxial cable without an antenna socket?
Of course.
When connecting additional devices (such as TVs) to a line, antenna sockets with several corresponding connections should be used. Alternatively, splitters with high decoupling between the outputs (>35dB) are suitable.
The “T-pieces” must not be used because they have no decoupling between the outputs. This can lead to reception interference with units connected in parallel.
Which antenna sockets can be used to connect the modem?
Our devices use the 2-200MHz frequency range for data transmission.
For this reason, multimedia sockets with a DATA port (frequency range 5-862MHz) are ideal for connecting modems. In principle, other ports (TV, Radio, SAT) can also be used if they are open in the 5-862MHz range. Sockets with ultra-wideband sockets (5-2400MHz) are also suitable.
Antenna sockets with DATA connections are offered by many manufacturers (Triax, Axing, Kathrein, Braun Telekom etc.) for all applications (SAT, Unicable SAT, cable TV).
The manufacturers usually specify the design of the socket connections in the data sheet. Example of a SAT socket with separate DATA connection – 4-hole socket Triax GAD404s:
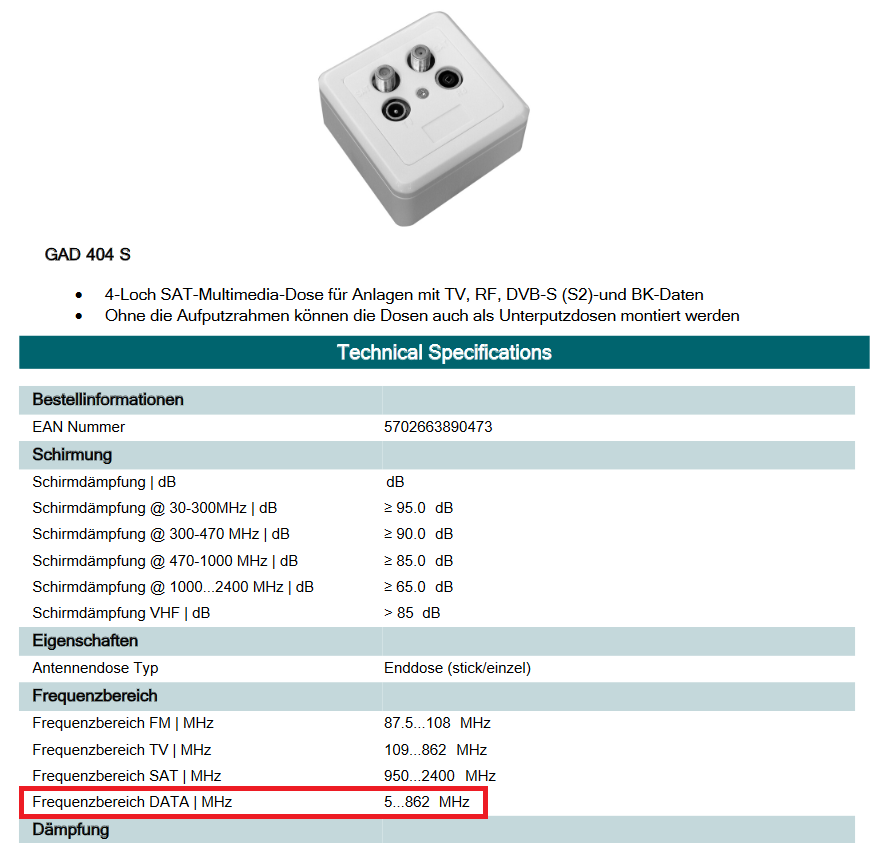
Example of a box with broadband TV and radio connections – Kathrein ESD30. TV and radio sockets are open in the range 5-862MHz, thus they correspond to a DATA connection and are suitable for the connection of the modem:

For the highest possible bandwidth, the DATA connection should have a low attenuation. For SAT sockets, DATA connections with max. 4-6dB are recommended.
Data networking in connection with cable TV (DVB-C) and cable Internet (DOCSIS)
Is parallel use of cable TV possible?
Yes, CATV channels in the 258-862MHz frequency range can be received in parallel with data networking.
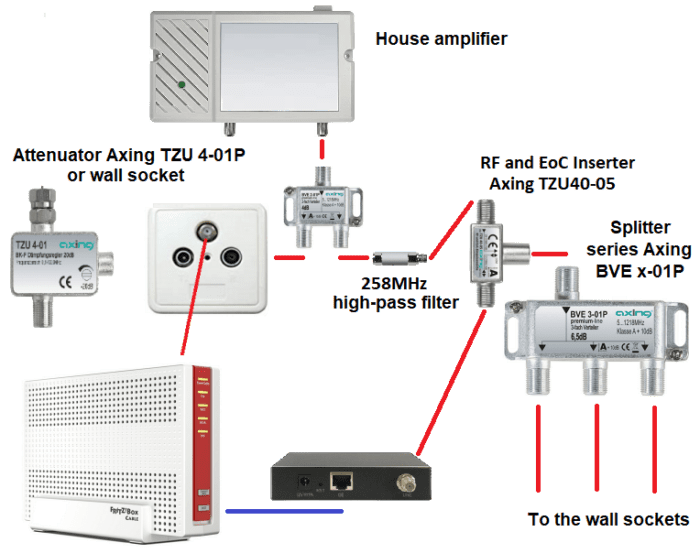
The TV and data signals are combined via an RF/EoC inserter. To avoid interferences in the cable network, an additional 258MHz high-pass filter must be used. The filter is usually installed at the output of the house amplifier or at the input of the coax splitter.
To connect TV devices a multimedia wall sockets with selective TV port (258-862MHz) must be used, e.g. Axing BSD 967-nnX (DOCSIS 4.0/3.1) series or Braun Telecom btv-MMD-5nn-d(s) series.

Note for apartment buildings: If there is a star-shaped sub-distribution in a flat with the help of a coaxial splitter, then data networking within the flat including cable TV reception is also possible. The EoC inserter and the high-pass filter are installed in the apartment before this splitter.
When using the 258MHz high-pass filter and the antenna socket with selective TV port (258-862MHz), the frequency assignment of the TV channels in the cable network should be observed. In order for the filter not to block any TV channels, they must be in the frequency range >258MHz. This is the case in most German areas and in many European countries.
How is data networking done in combination with cable internet (DOCSIS)?
G.hn uses the lower frequencies 2-200MHz for data transmission. Cable internet (DOCSIS), on the other hand, occupies the entire terrestrial frequency range 5-862MHz. Both signals overlap and can therefore not be transmitted in parallel on one coaxial cable.
For home networking with our devices, the Internet reception must be separated from the rest of the coaxial data network in the house.
To do this, the Internet router must be connected near the house amplifier.
This sketch shows the procedure without CATV:
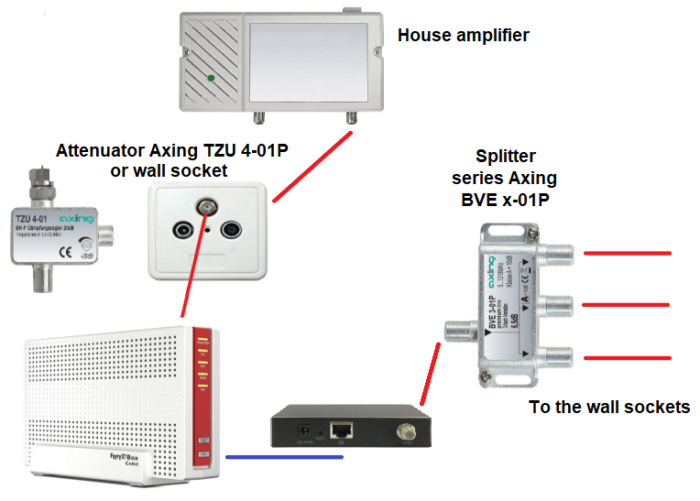
This sketch shows the connection including CATV channels in the 258-862MHz frequency range. To connect TV devices a multimedia wall sockets with selective TV port (258-862MHz) must be used, e.g. Axing BSD 967-nnX (DOCSIS 4.0/3.1) series or Braun Telecom btv-MMD-5nn-d(s) series.